Astronomy News
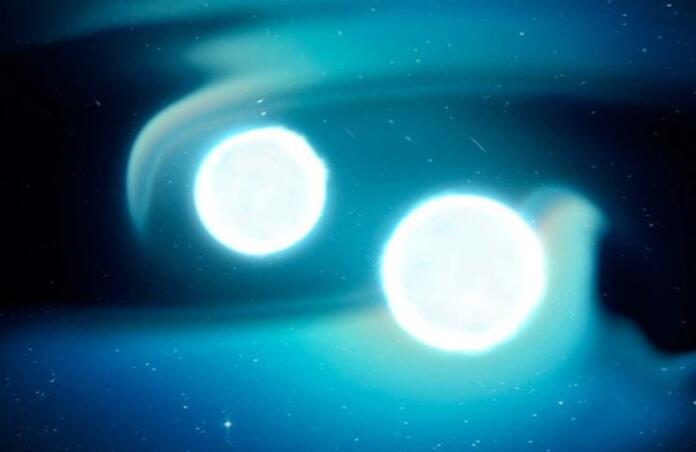
Discovery of White Dwarf Binary Fated for Double-Detonation Event
Type Ia supernovae are a crucial class of astronomical events in the study of cosmology, due to their use as standard candles.
0
0